- Location : Home» Newsroom
Mapping the Phosphorylation Regulatory Network of Single-celled Fiber Elongation Mediated by GhBIN2 in Cotton
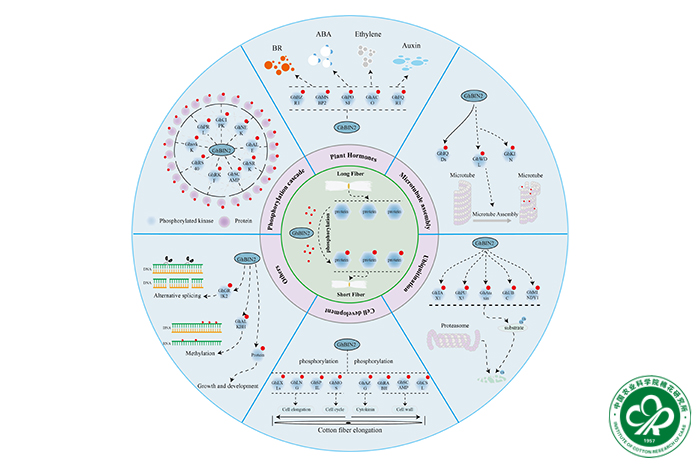
Protein phosphorylation plays a pivotal role in cellular signal transduction and plant development. The plant steroid hormoneBrassinosteroids (BRs) signal transduction relies primarily on protein kinase-mediated phosphorylation cascades. However, thespecific mechanisms of phosphorylation regulation in BR signalling remain to be fully elucidated. This study focuses on BIN2, anindispensable protein kinase in the BR signalling pathway, utilising single-celled cotton fibre to investigate the mechanisms bywhich phosphorylation regulates cell elongation. Firstly, we confirmed the inhibitory role of GhBIN2 in fibre elongation throughits overexpression. Subsequently, we employed 4D-fastDIA quantitative phosphoproteomics and proteomics analysis to map theGhBIN2-mediated phosphorylation regulatory network. Through a comprehensive analysis of this network, we identified sixcredible substrates of GhBIN2. Further investigation revealed that GhBIN2 interacts with substrate GhIQD14 and increases itsabundance through phosphorylation to negatively regulate fibre elongation. This study deepens the understanding of BR signal-ling in cotton fibre elongation and provides experimental evidence and new insights for comprehending the regulatory role ofprotein phosphorylation in plant cell elongation processes.