- Location : Home» Newsroom
A telomere-to-telomere genome assembly of cotton provides insights into centromere evolution and short-season adaptation
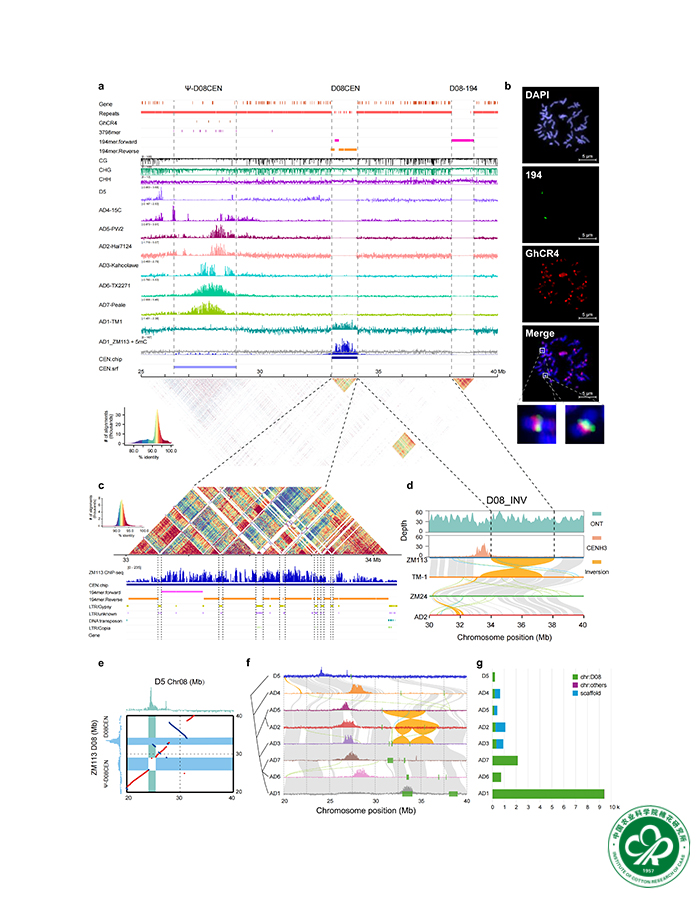
Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) is a key allopolyploid crop with global economic importance. Here we present a telomere-to-telomere assembly of the elite variety Zhongmian 113. Leveraging technologies including PacBio HiFi, Oxford Nanopore Technology (ONT) ultralong-read sequencing and Hi-C, our assembly surpasses previous genomes in contiguity and completeness, resolving 26 centromeric and 52 telomeric regions, 5S rDNA clusters and nucleolar organizer regions. A phylogenetically recent centromere repositioning on chromosome D08 was discovered specific to G. hirsutum, involving deactivation of an ancestral centromere and the formation of a unique, satellite repeat-based centromere. Genomic analyses evaluated favorable allele aggregation for key agronomic traits and uncovered an early-maturing haplotype derived from an 11 Mb pericentric inversion that evolved early during G. hirsutum domestication. Our study sheds light on the genomic origins of short-season adaptation, potentially involving introgression of an inversion from primitively domesticated forms, followed by subsequent haplotype differentiation in modern breeding programs.